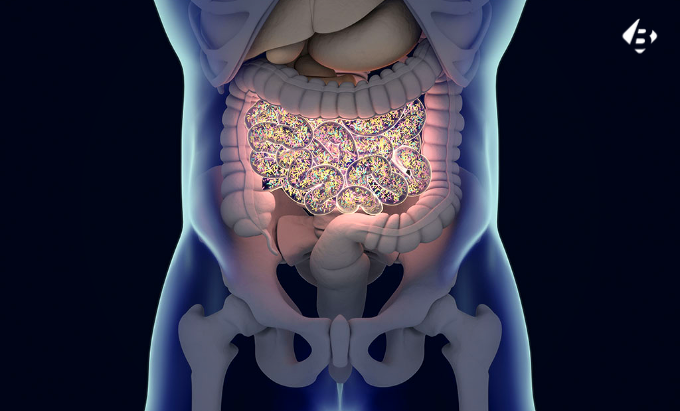
The human body is home to a vast ecosystem of microbes, collectively known as the microbiome. This intricate network of bacteria, fungi, and viruses plays a crucial role in our health and well-being, influencing everything from digestion and immunity to metabolism and mental health. In recent years, a revolutionary field of research has emerged, focusing on harnessing the power of the microbiome to treat a wide range of health conditions.
Unveiling the Therapeutic Potential:
Microbiome-based therapies offer a promising new approach to healthcare, with potential applications in various areas:
1. Gastrointestinal Disorders:
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): Studies suggest that fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) can effectively alleviate symptoms of IBS, including abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): FMT has also shown promising results in treating Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, reducing inflammation, and improving disease activity.
- Clostridium difficile infection (C. diff): FMT is a highly effective treatment for C. diff infection, with success rates exceeding 90%.
2. Metabolic Disorders:
- Obesity: Research suggests that gut bacteria may play a role in regulating weight and metabolism. Microbiome-based therapies could potentially help individuals manage weight and reduce the risk of obesity-related diseases.
- Type 2 diabetes: Studies indicate that modifying the gut microbiome may improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control, offering a potential treatment approach for type 2 diabetes.
3. Mental Health:
- Depression: Emerging evidence suggests a link between gut bacteria and mental health. Microbiome-based therapies may offer a novel approach to treating depression and anxiety disorders.
4. Skin Conditions:
- Eczema: Research suggests that imbalances in the gut microbiome may contribute to eczema development. Probiotics and other microbiome-modulating interventions could be beneficial in managing eczema symptoms.
5. Cancer:
- Immunotherapy: Studies suggest that gut bacteria can influence the effectiveness of immunotherapy in cancer treatment. Researchers are exploring how to modulate the microbiome to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy and improve patient outcomes.
Exploring Different Therapeutic Approaches:
Several strategies are being explored to harness the power of the microbiome for therapeutic purposes:
- Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT): This involves transplanting gut bacteria from a healthy donor to a recipient, aiming to restore a healthy microbial balance.
- Probiotics: These are dietary supplements containing live bacteria that offer various health benefits.
- Prebiotics: These are food components that promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Postbiotics: These are non-living products produced by bacteria, such as short-chain fatty acids, which offer health-promoting effects.
- Microbiome-modulating drugs: These drugs target specific gut bacteria or their products to induce desired therapeutic effects.
Challenges and the Road Ahead:
While the potential of microbiome-based therapies is vast, several challenges need to be addressed:
- Limited research and clinical data: More research is needed to fully understand the complex interactions between the microbiome and various health conditions.
- Standardization and regulation: Lack of standardization in FMT and other microbiome-based therapies necessitates regulatory frameworks to ensure patient safety and efficacy.
- Cost and accessibility: Making these therapies accessible and affordable for all patients remains a challenge.
- Individual variability: The diverse composition of the human microbiome requires personalized approaches to optimize therapeutic effects.
Conclusion:
Microbiome-based therapies hold immense promise for revolutionizing healthcare. By understanding the intricate relationship between gut bacteria and human health, we can unlock new avenues for treating a wide spectrum of diseases. As research continues and challenges are overcome, we can look forward to a future where personalized microbiome-based interventions become a cornerstone of preventive and therapeutic healthcare, empowering individuals to achieve optimal health and well-being.
Exploring the microbiome’s therapeutic potential is truly a game-changer. From gastrointestinal to mental health conditions, the applications are diverse. Addressing challenges in research, regulation, and accessibility will shape the future of microbiome-based healthcare.
The microbiome’s impact on health is astounding, and leveraging it for therapies is revolutionary. The potential to treat conditions like diabetes and mental health disorders is promising. As we navigate challenges, personalized microbiome interventions could redefine healthcare.
The microbiome’s role in health is fascinating! The potential for microbiome-based therapies to treat conditions from IBS to mental health is groundbreaking. Overcoming challenges like standardization and accessibility will be key to realizing this revolution in healthcare.
Microbiome-based therapies open new frontiers in healthcare. From gastrointestinal to cancer treatments, the possibilities are exciting. Tackling challenges like standardization and cost will be crucial for translating this research into accessible, personalized interventions.